1 Example Application
1.1 Slot Filling
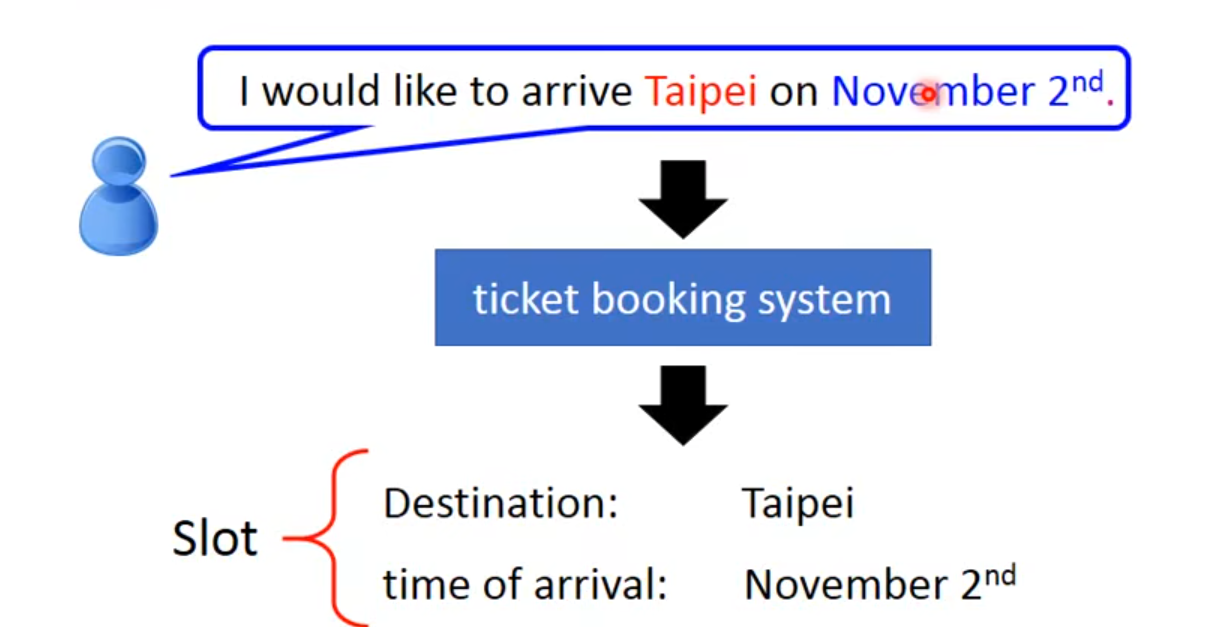
👆句子中只有Taipei和November $2^{nd}$ 属于两个slot中,其余词汇不属于任何slot
1.2通过feedforward network实现slot filling
Input : a word
(Each word is represented as a vector):
- 1-of-N encoding
- beyond 1-of-N encoding
- dimension for “other”:在1-of-N encoding多加一个dimension,这个dimension代表other(没见过的词汇)
2.word hashing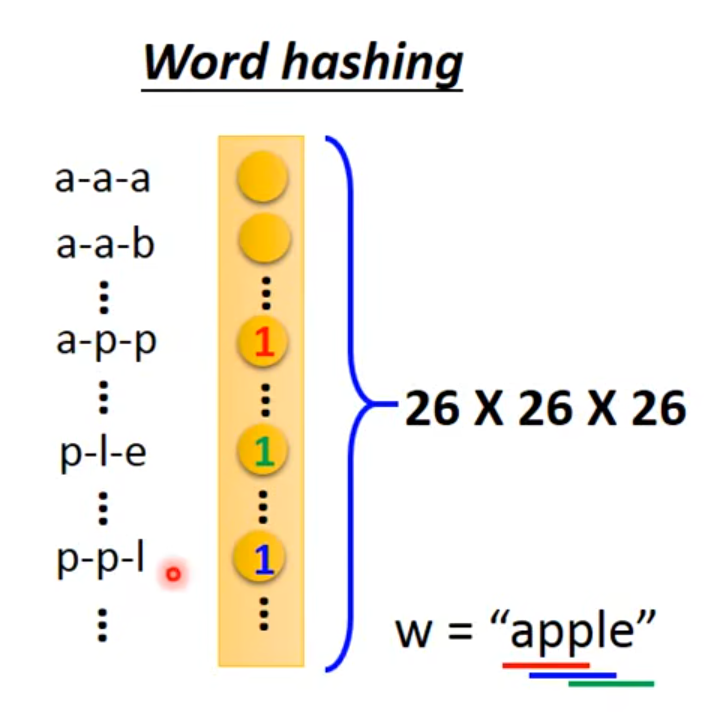
- dimension for “other”:在1-of-N encoding多加一个dimension,这个dimension代表other(没见过的词汇)
Output:probability distribution that the input word belonging to the slots
1.3Problem
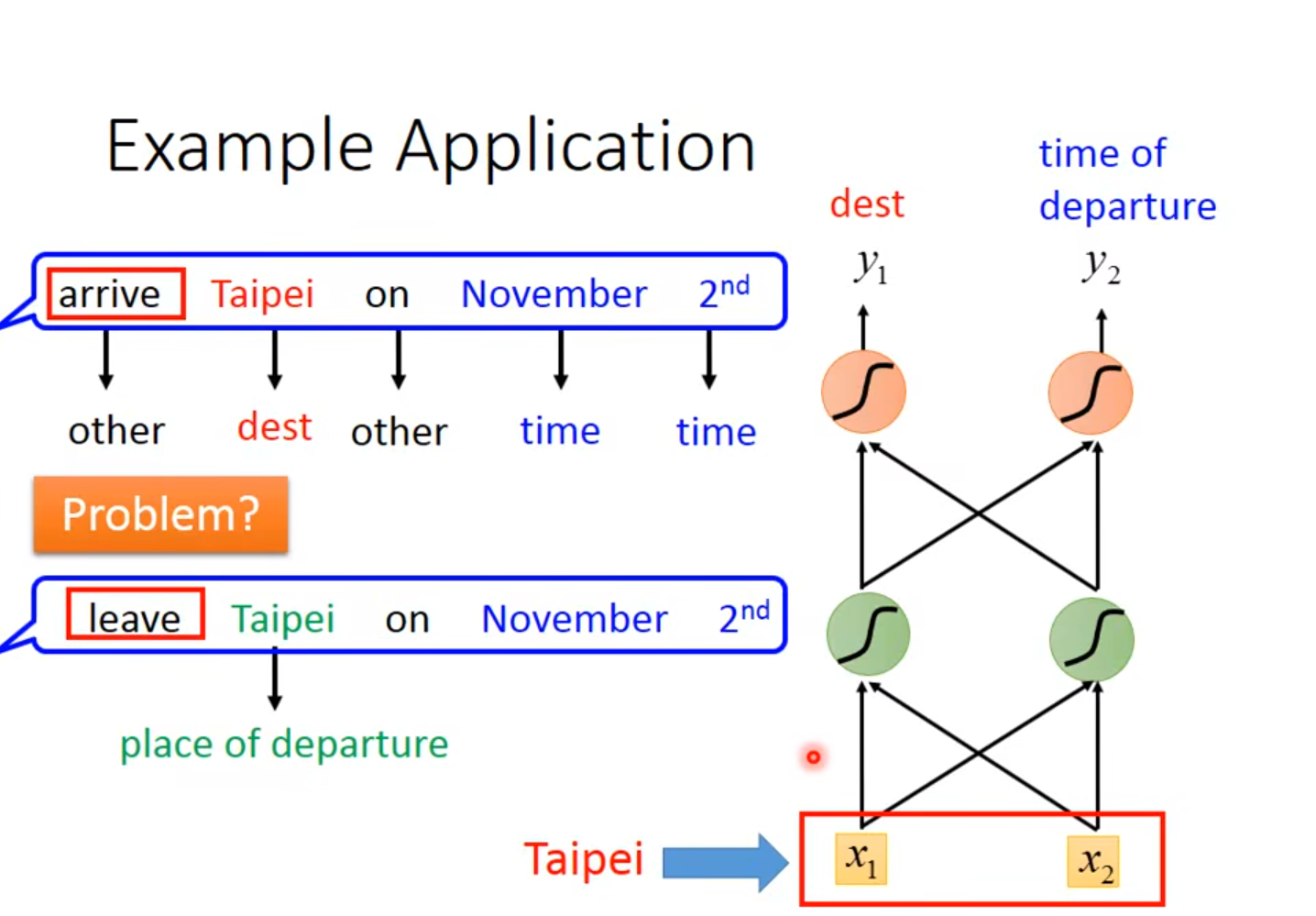
input Taipei这个词汇,要么都是destination几率最高,要么都是place of departure几率最高👉我们希望nerual network是有记忆力的👉如果他能记住arrive和leave那他的output就可以不同
1.4 Solution
使用Recurrent Neural Network时,要先给memory的起始值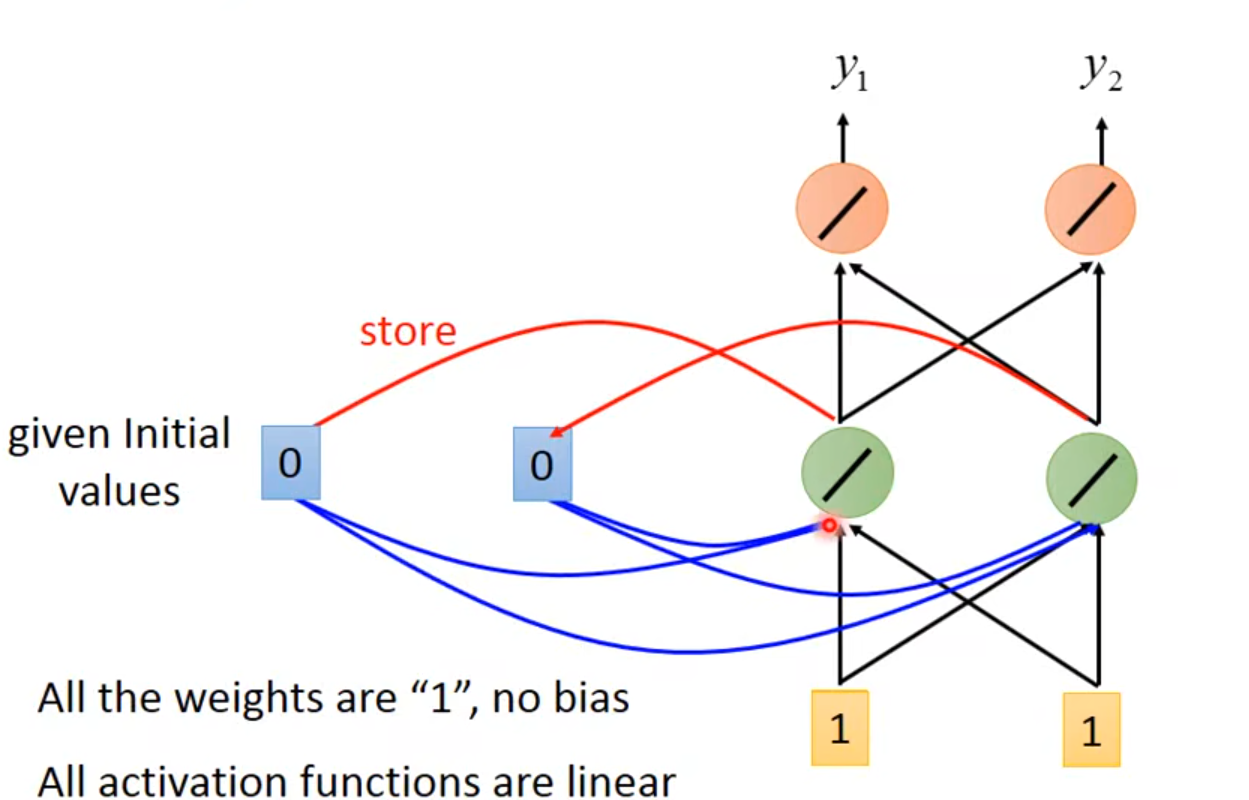
👆初始值为0,输入为1,绿色neuron接收1、1和0、0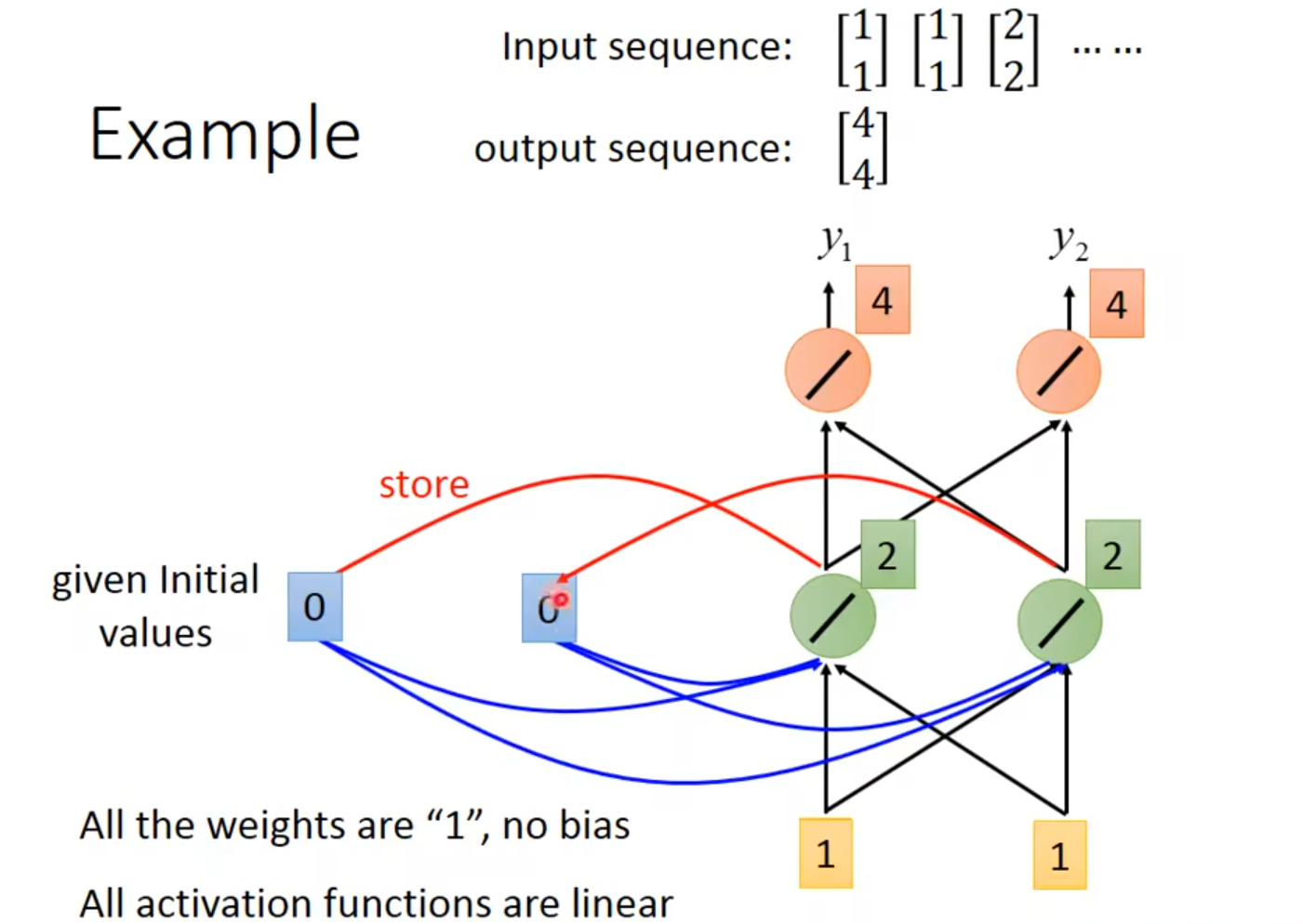
👆$y_1=4$、$y_2=4$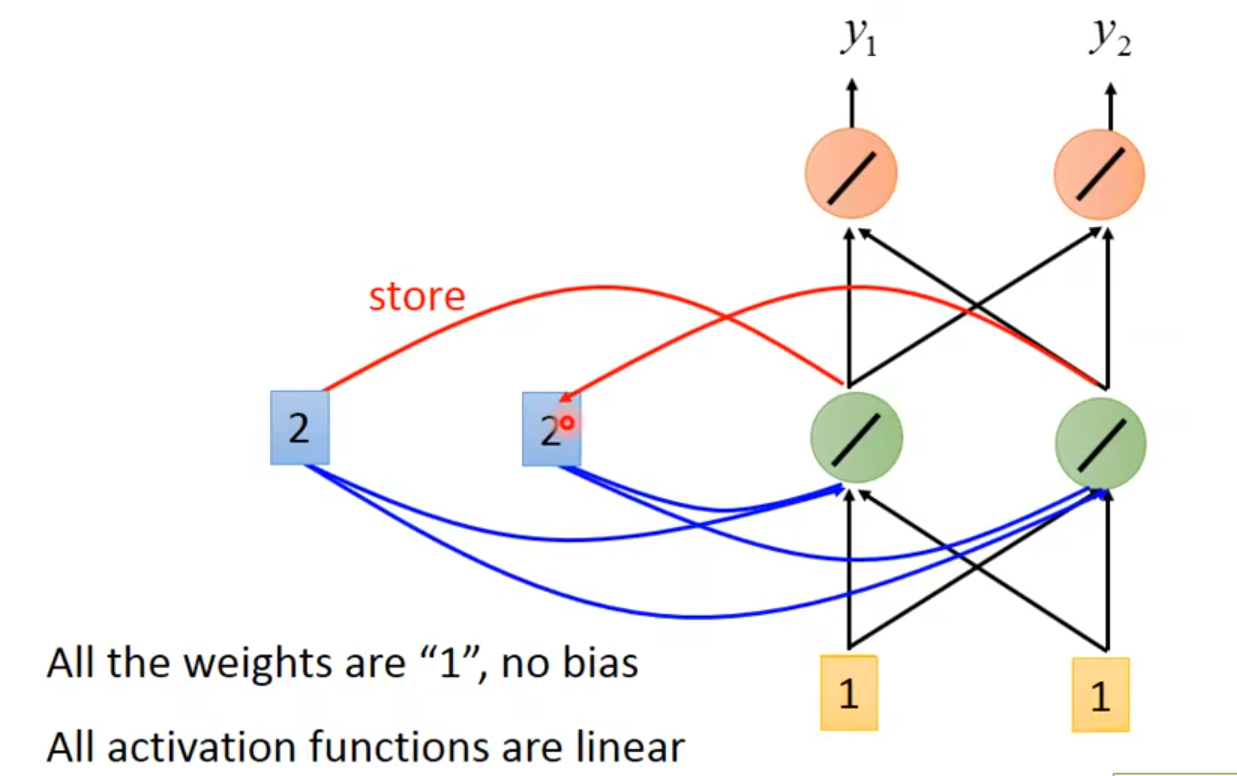
👆绿色neuron里memory的值变成2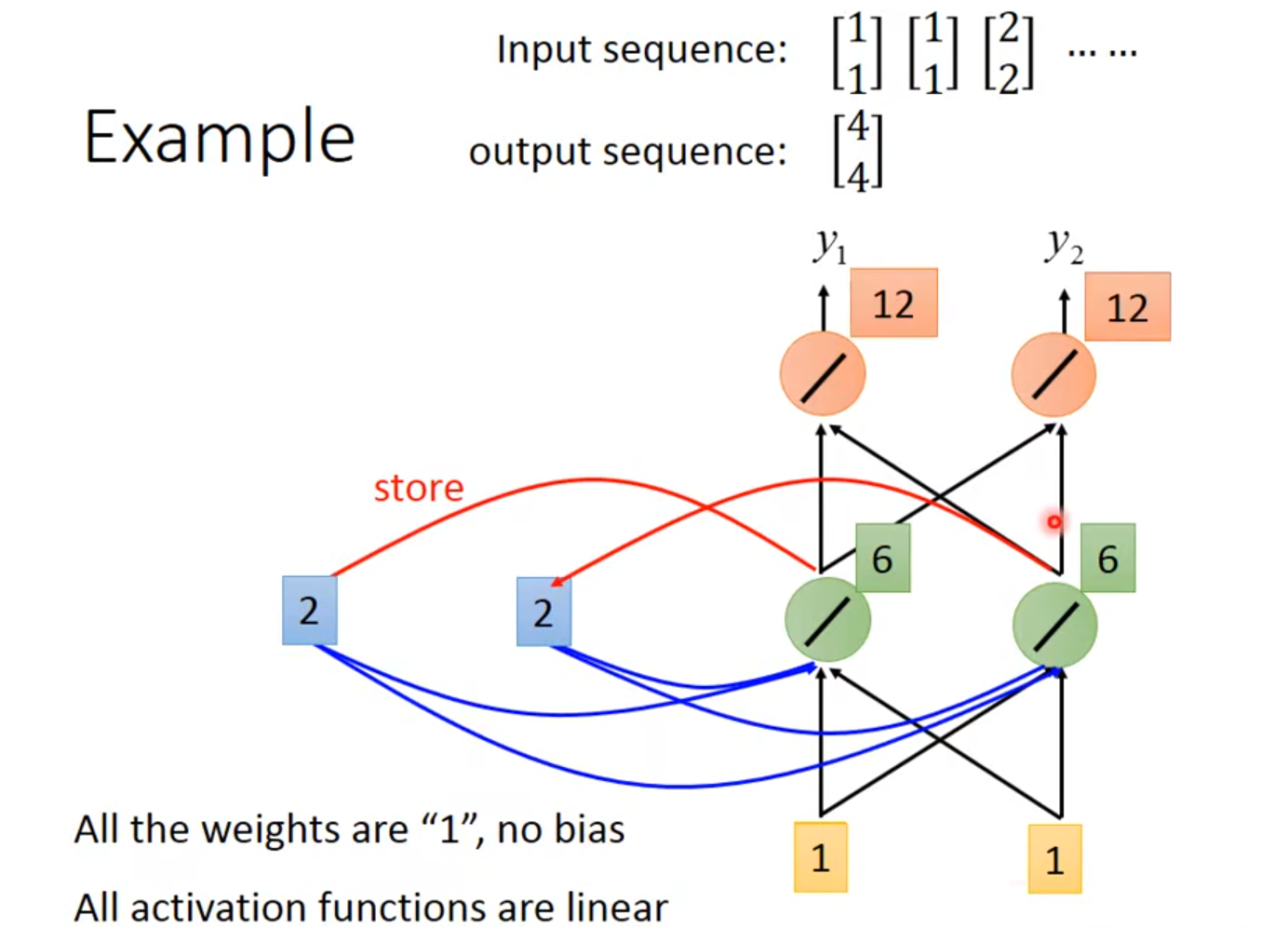
👆第二次输入[1,1]
如果input的顺序不一样,output的内容也会不一样
总况: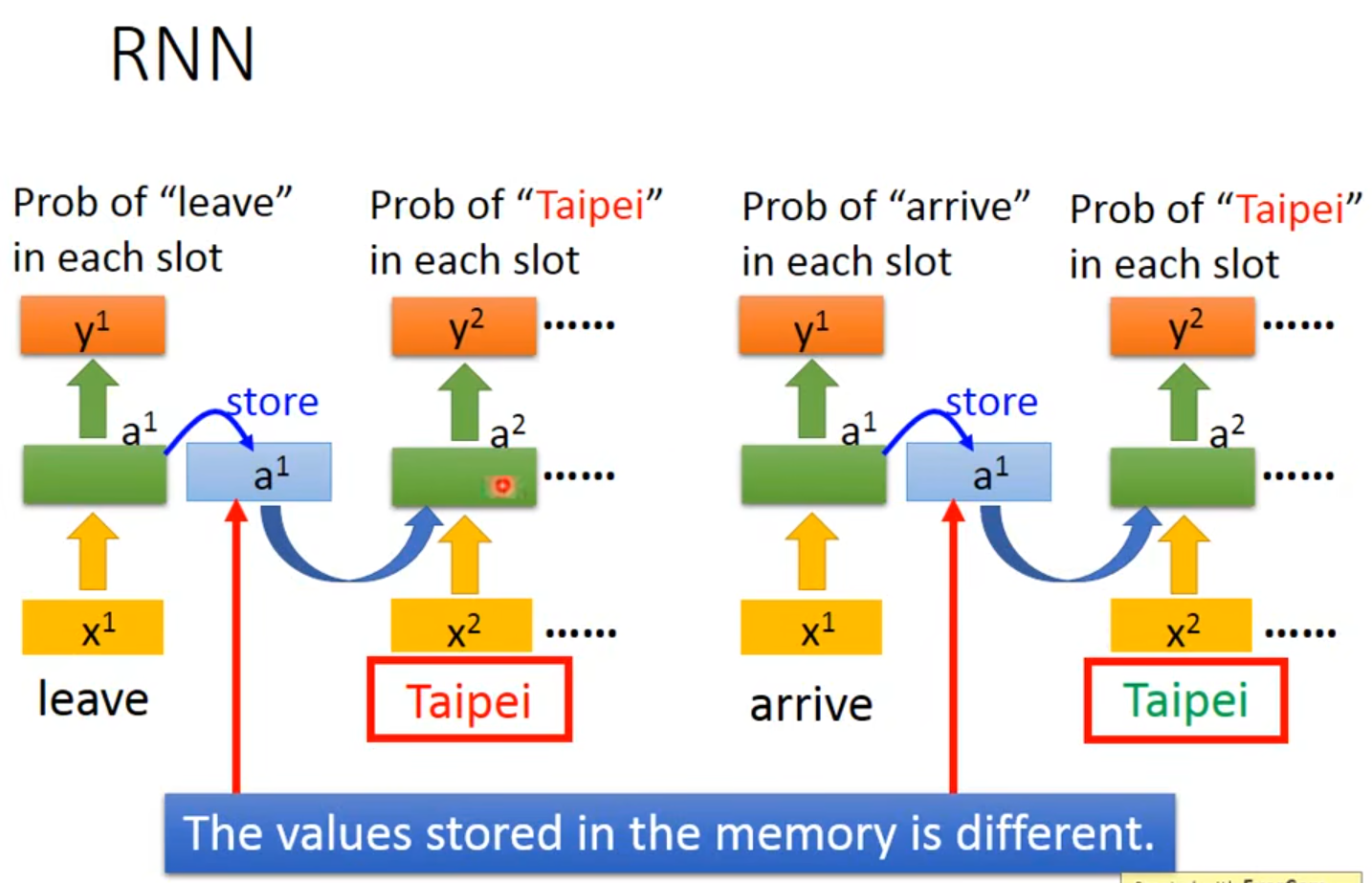
在memory中store不同的values使得Taipei的slot不同,一个是destination一个是place of departure
2 Deep hidden layer RNN
👇每一个绿色框是一个hidden layer,蓝色箭头是hidden layer的值memory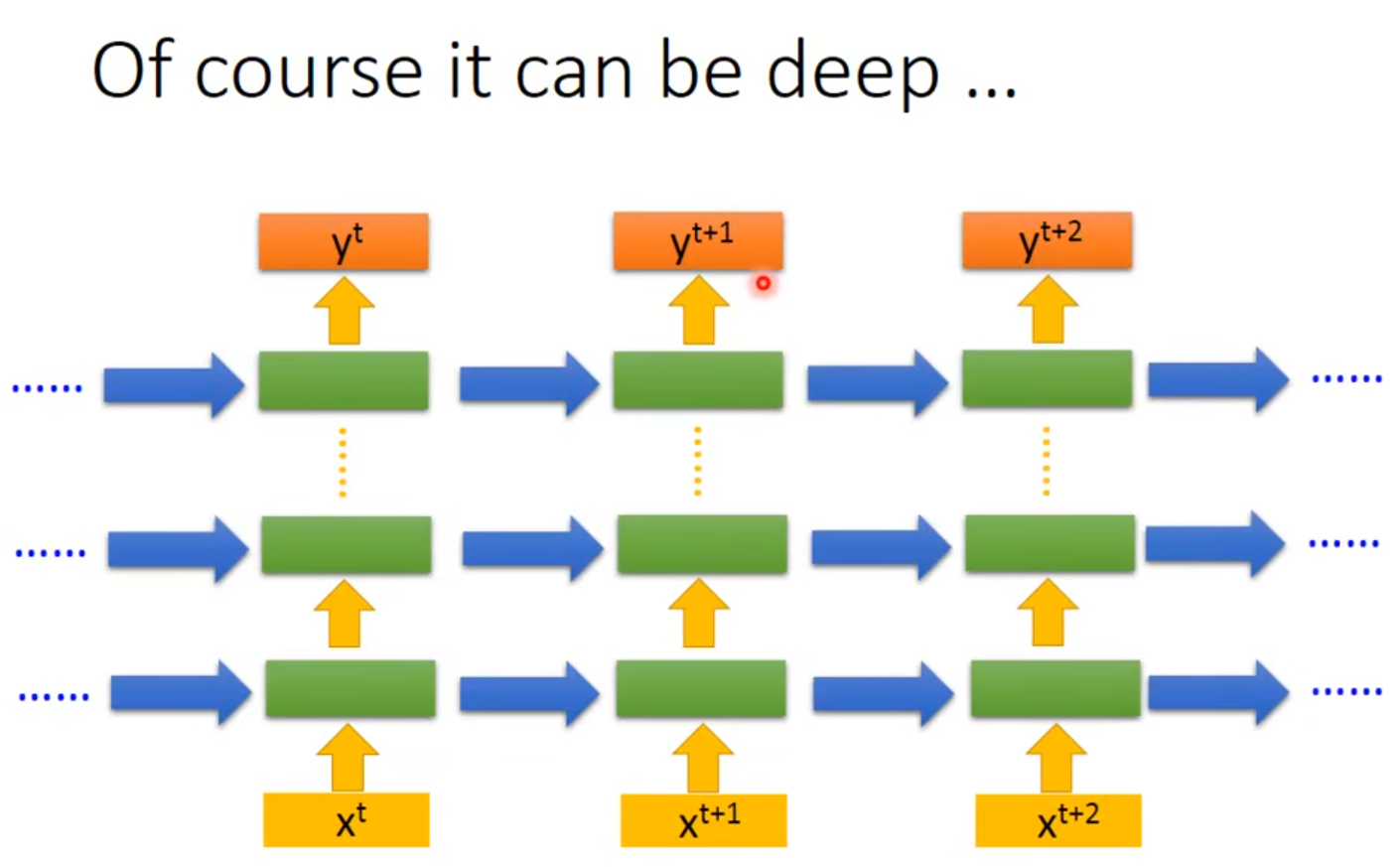
2.1 Elman Network
👇hidden layer的值先存起来,下一个时间点再读出来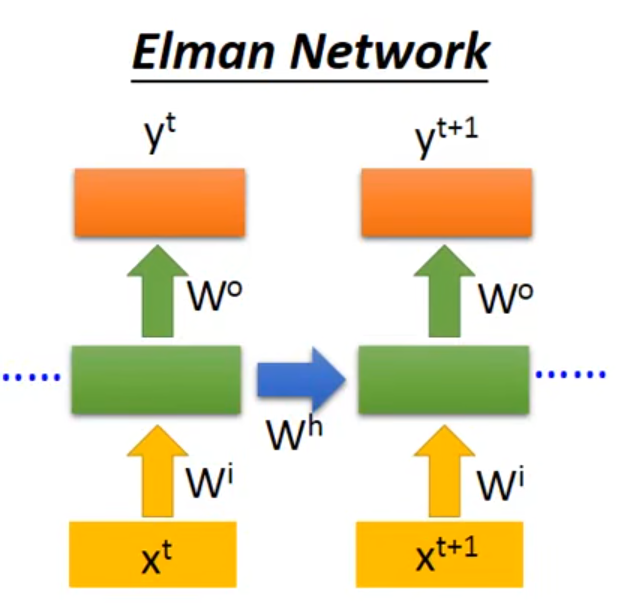
2.2 Jordan Network
👇把output的值先存在memory里面,下一个时间点再读出来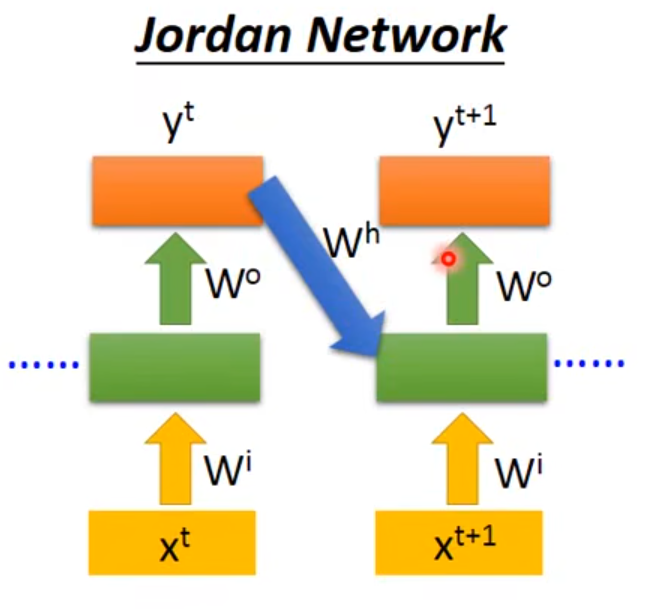
2.3 Bidirectional RNN
👇同时train正向和逆向的RNN,把正向和逆向的output都丢到output layer产生$y^t$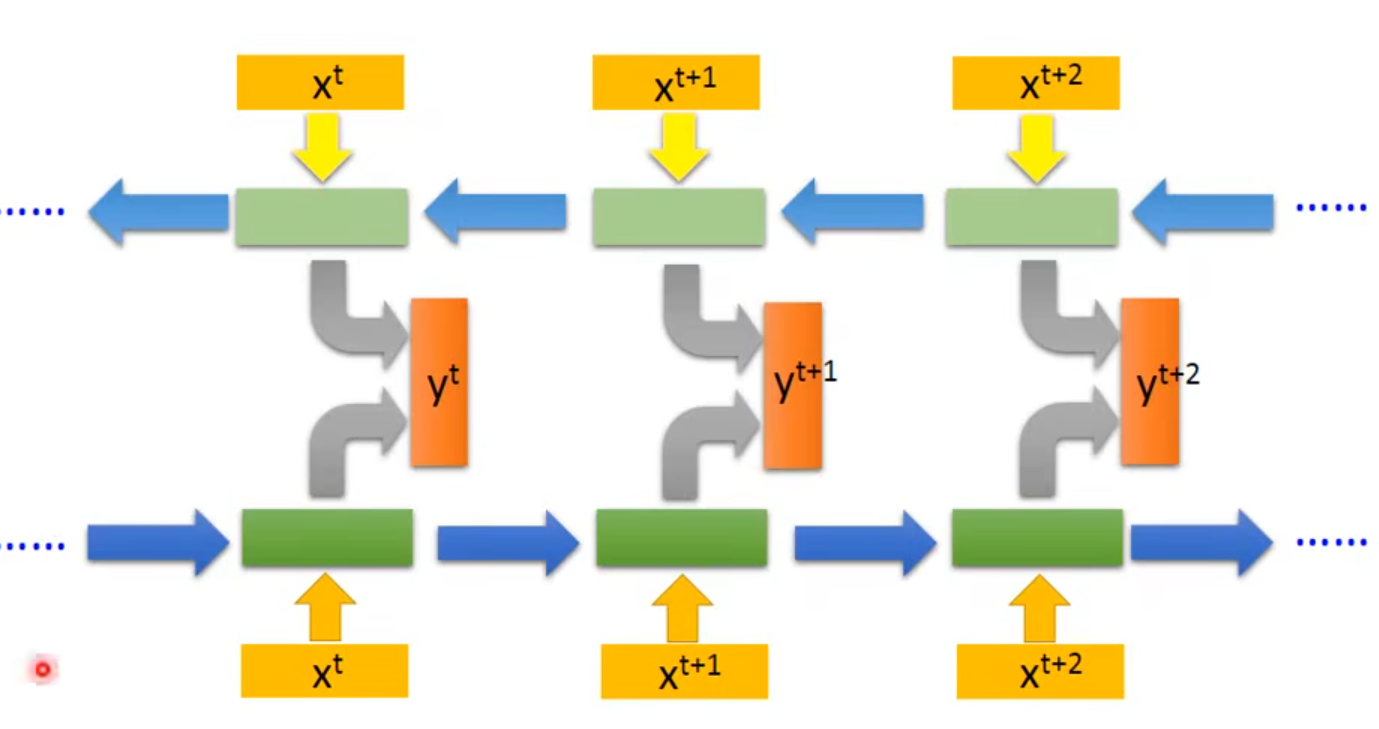
相当于看了整个sequence
3 Long Short-term Memory
4 input:①想要存到memory中的值 ②操控Input Gate的信号 ③操控Output Gate的信号 ④操控Forget Gate的信号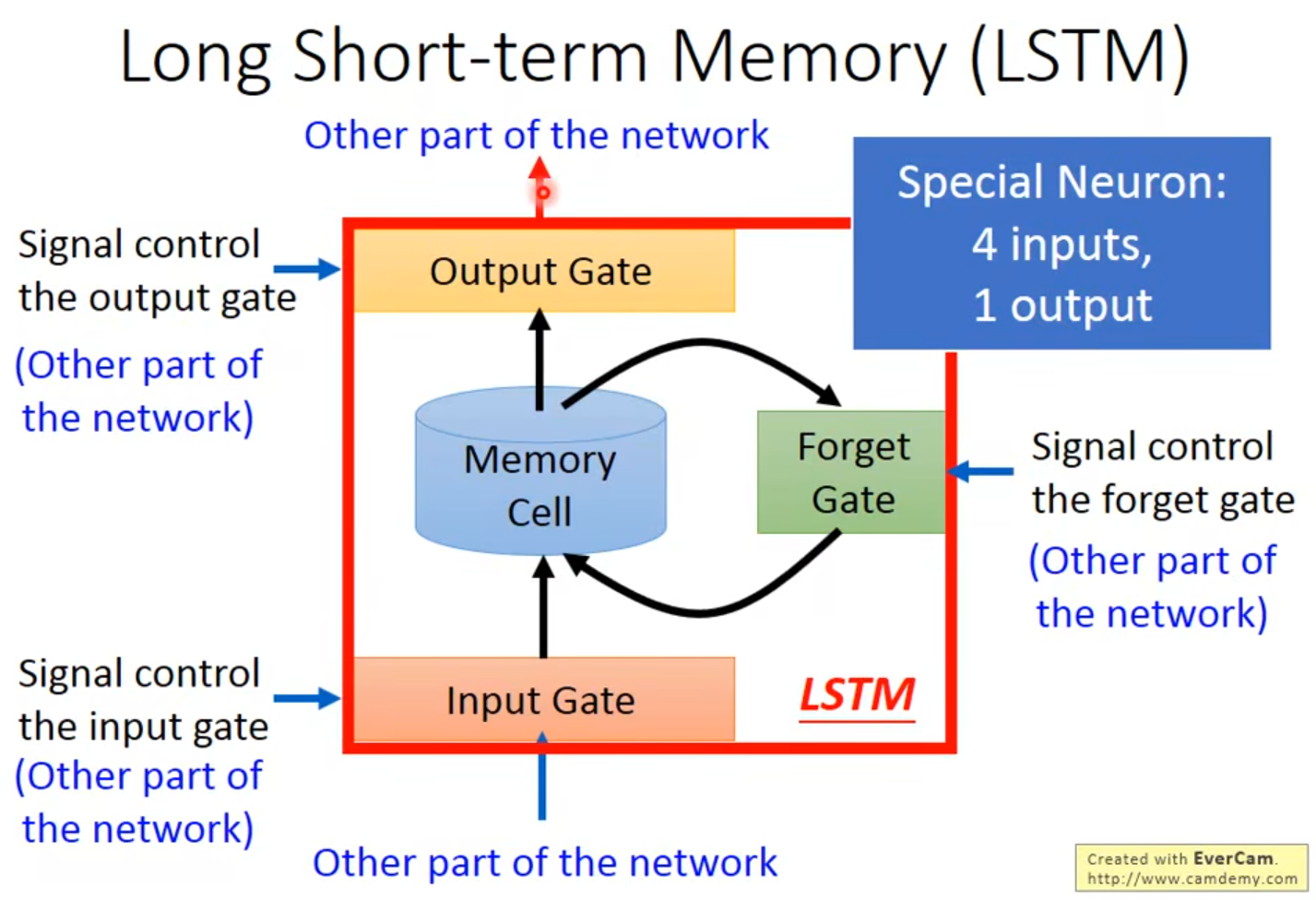
$f(z_i)$决定$g(z)$能否输入
Forget Gate被关闭,即$f(z_f)$数值为0时代表遗忘,反之为记忆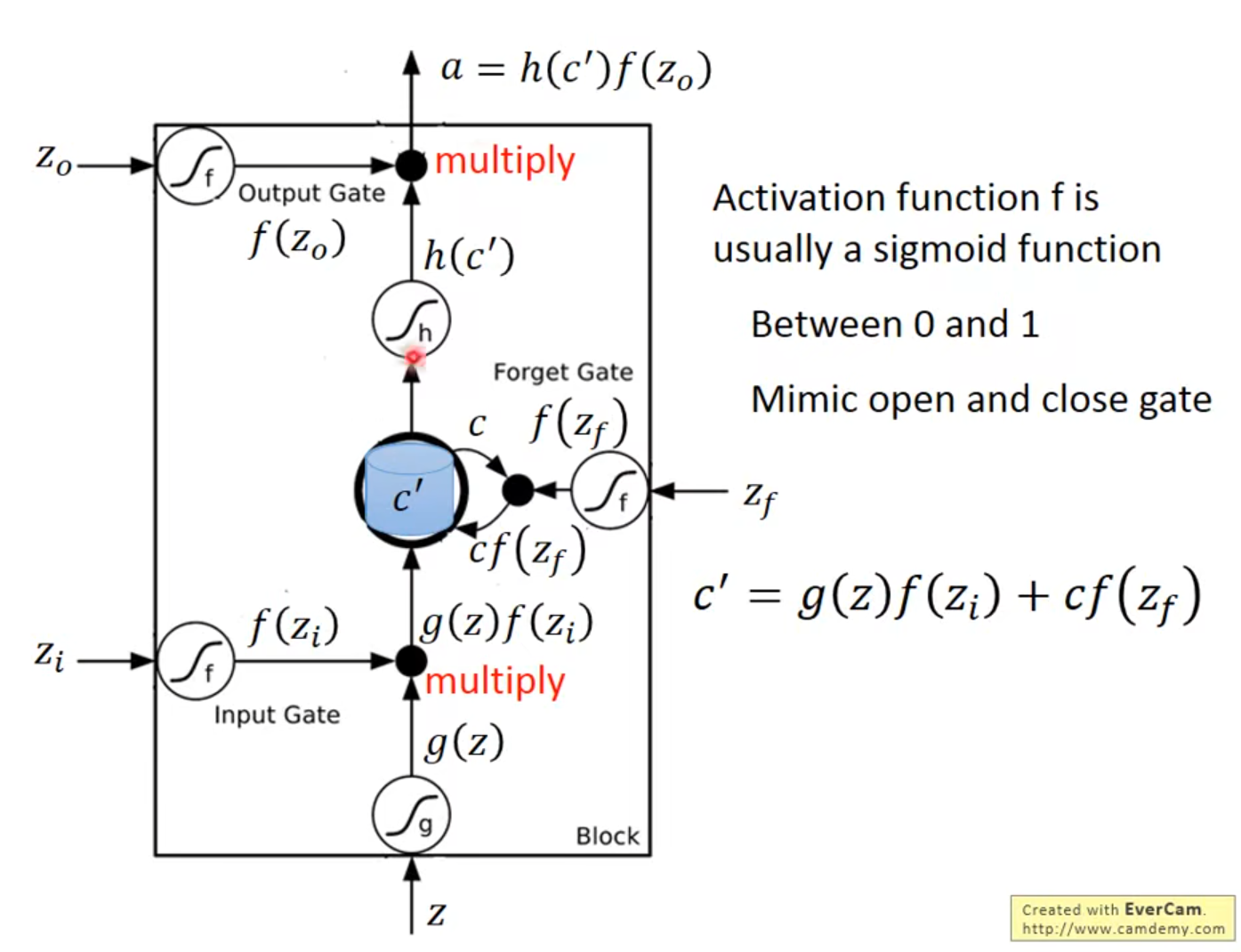
3.1 LSTM - Example
t时刻对memory的影响会在t+1时刻体现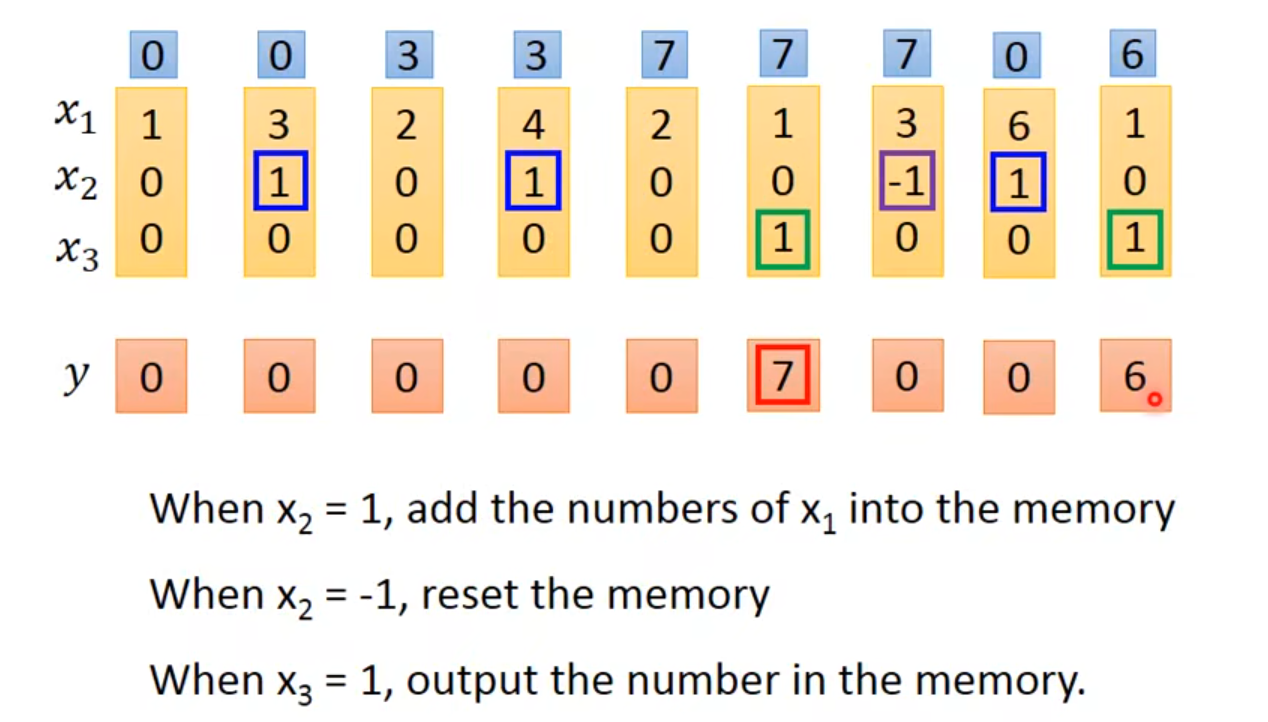
weight 和 bias用training data通过gradient descent得到的
LSTM vs original network: 4 times of parameter
- *$x^t$乘上一个transform得到vector$z$,vector$z$的每一个dimension操控每一个LSTM的input,$z$的dimension数目=LSTM memory cell的数目,$z^i$、$z^o$、$z^f$同理
- *$z^i$、$z^o$、$z^f$、$z$丢到cell里的值只是他们其中的一个dimension
- $c^{t-1}$、$h^{t-1}$、$x^t$一起乘transform然后作为输入
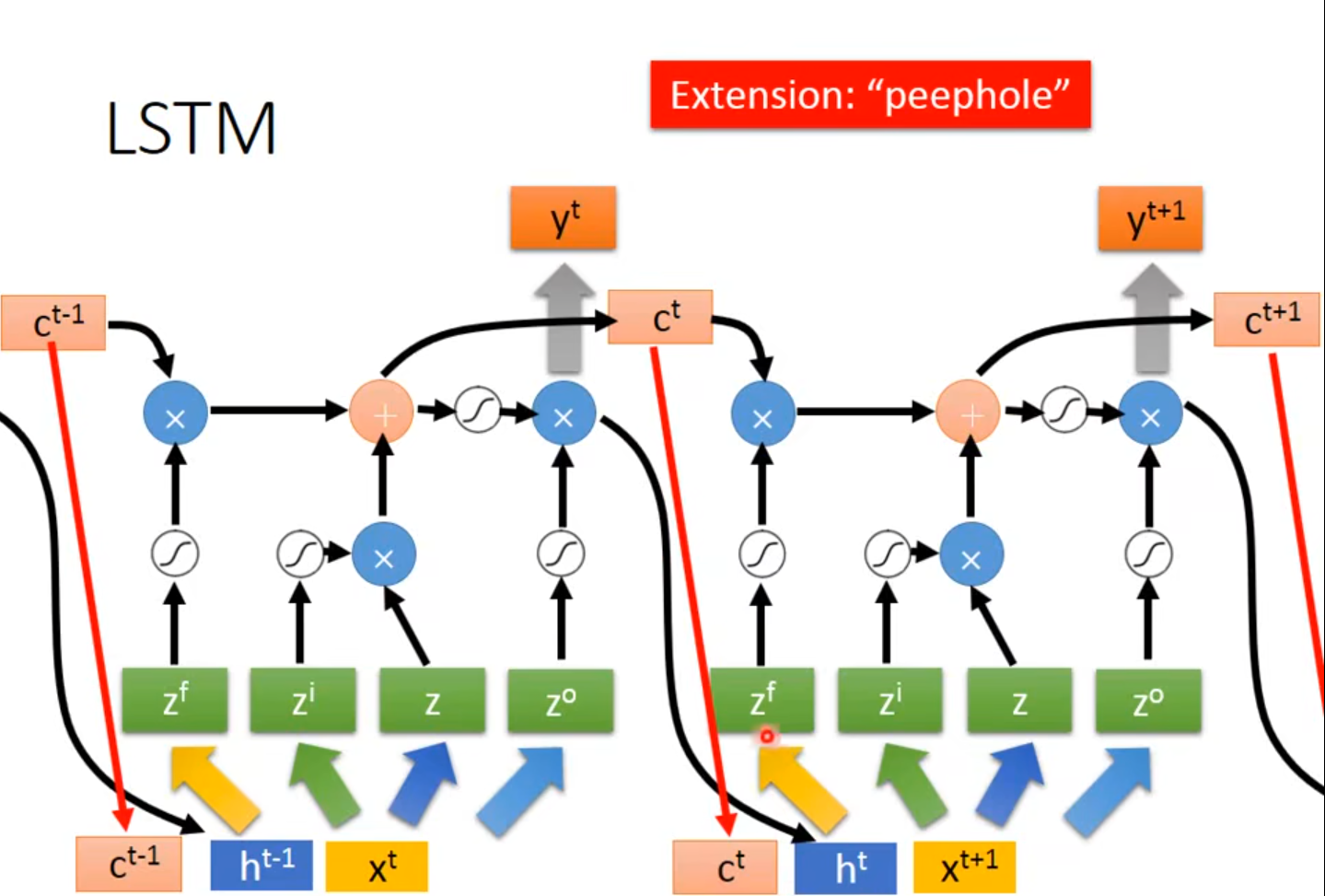
3.2 Learning Target
有一个training sentence,要给sentence里的每一个word一个label
👇输入arrive得到一个vetor,vetor中dimensionother的值为1,其余为0。在丢$x^2$之前要先丢$x^1$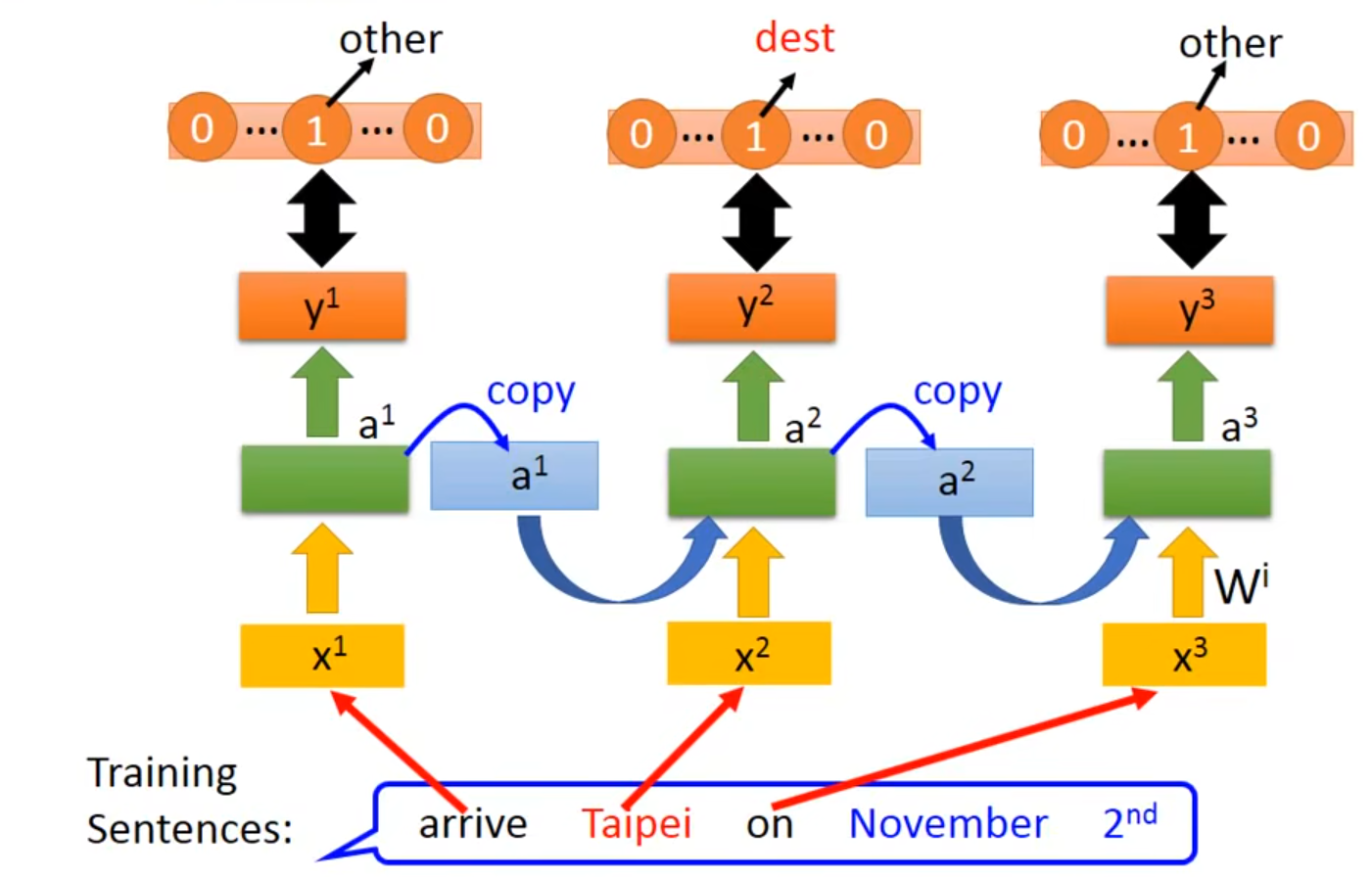
reference vector(红色那条)的长度就是slot的数目
👇RNN可以用gradient descent train出来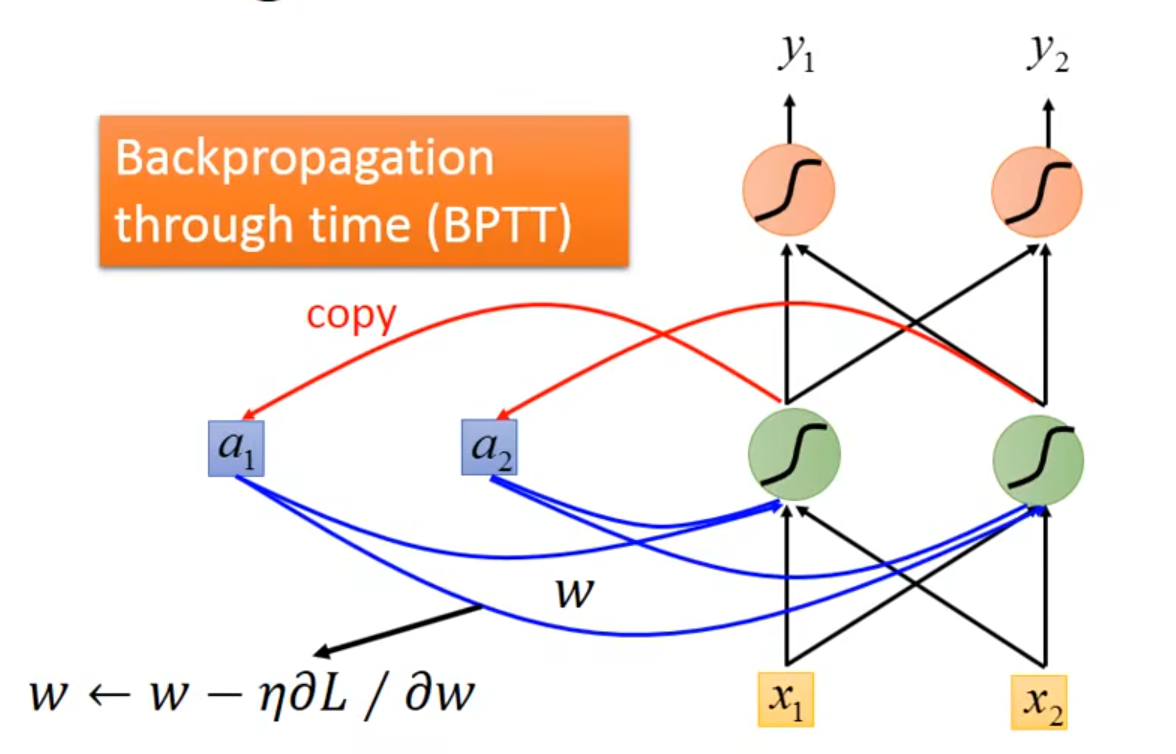
3.3 Problem
👇RNN-based network is not always easy to learn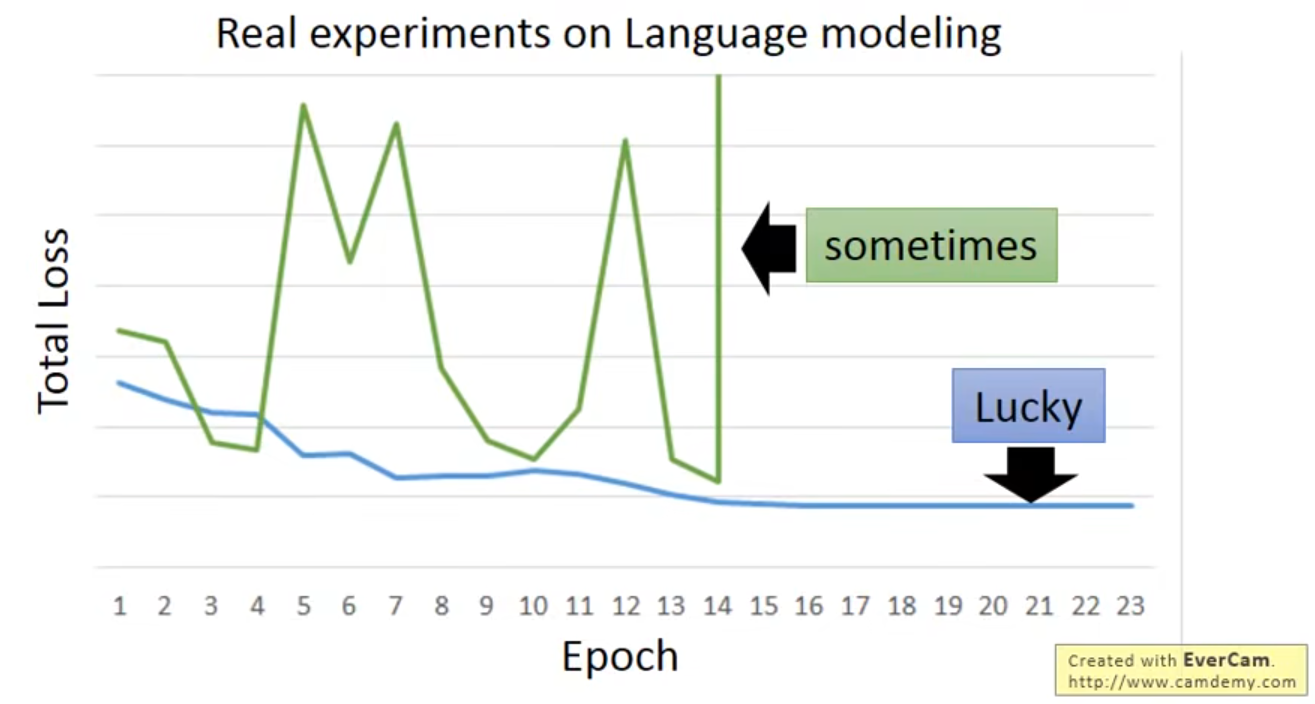
👇从最右边的橙色点update到中间的再update到左边的橙色点,Total Loss突然暴增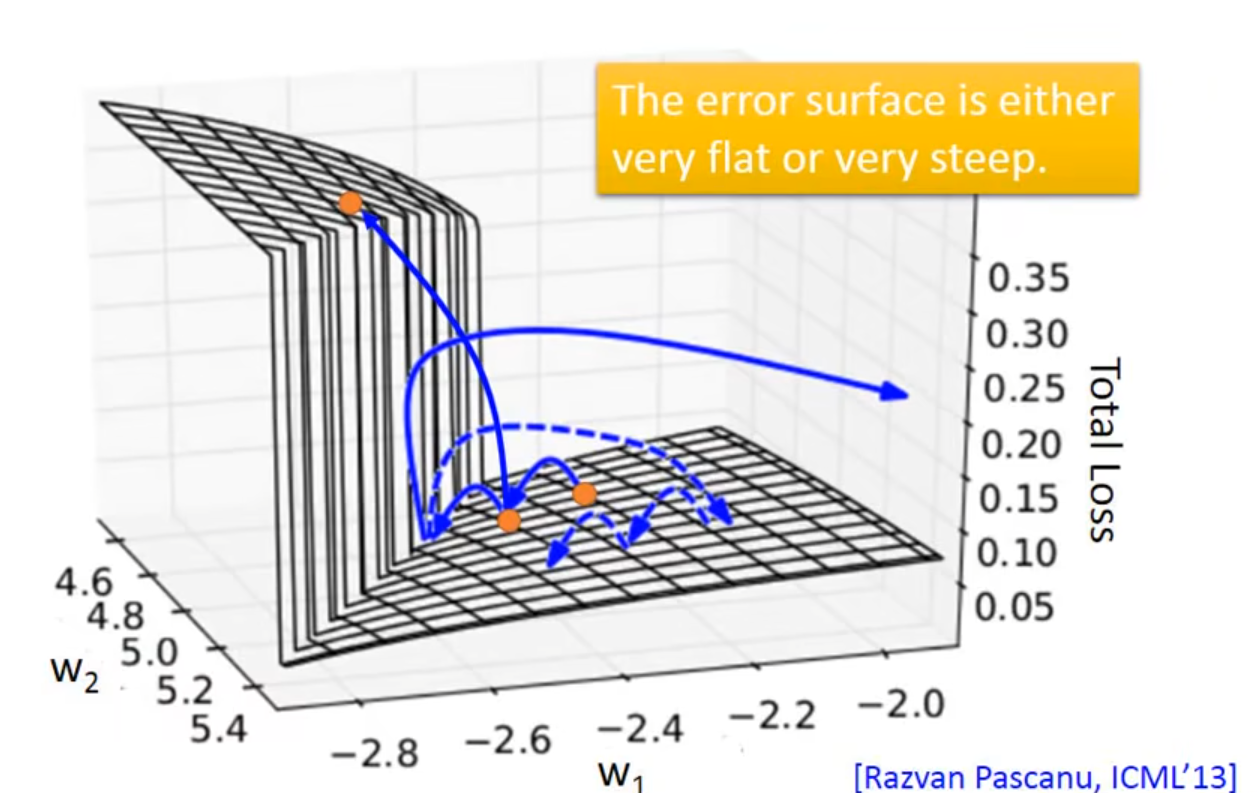
👇Error Surface 最左边橙色的点的位置的gradient很大,一开始的gradient很小,learning rate有可能设置得很高,导致$gradient$ x $learning$ $rate$会很大,就像开飞机一样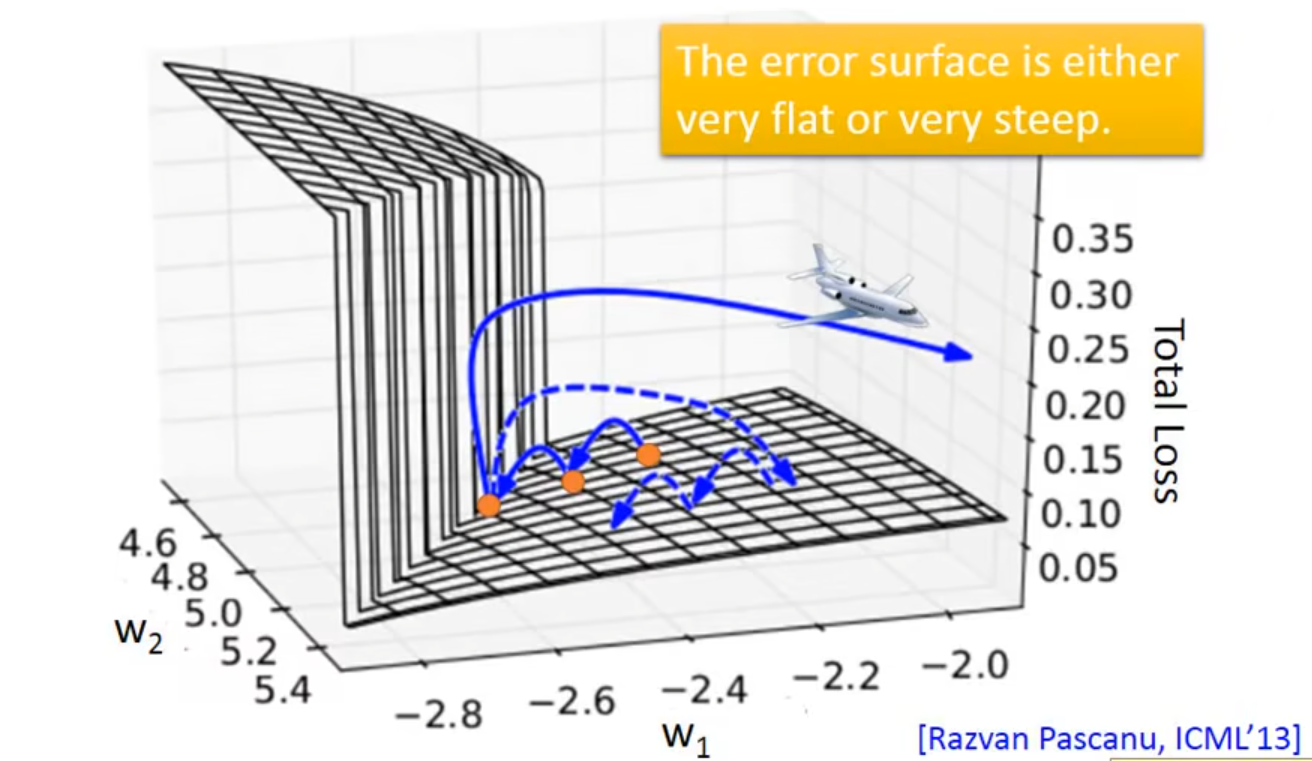
👆解决办法:设置threshold value,当gradient大于某值时将gradient设置为某值
RNN的问题在于time sequence的weigh在不同的时间点会被反复使用
👇$w$等于$1$、$1.01$、$0.99$、$0.01$时,$y$的取值变化都会很大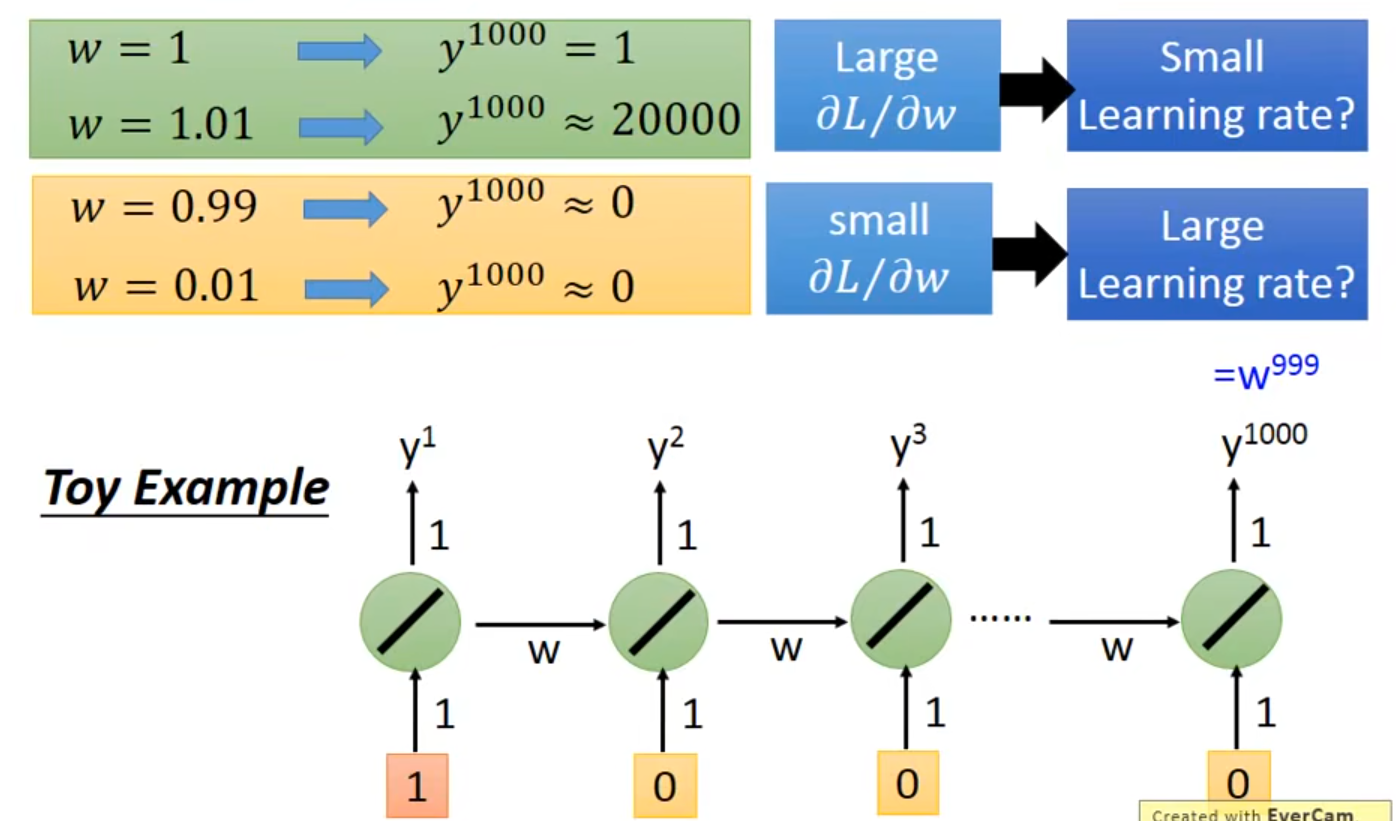
3.4 Solution
LSTM
- Can deal with gradient vanishing(not gradient explode) 不会出现error surface很平坦的地方,可以解决梯度消失的问题👉所以learning rate可以设置得小一点
- RNN vs LSTM
- RNN中每个时间$t$ memory的值会被覆盖掉
- LSTM中
- 每个时间$t$ menory and input are added👉解决梯度消失
- The influence never disappears unless forget gate is closed,只有foget gate关上才有可能导致LSTM不断更新input和memory的值
- No gradient vanishing(If forget gate is opened)
4 More Applications
4.1 Sequence-to-sequence
- Input is a vector sequence, but output is only one vector(Many to One)
- Sentiment Analysis
- Key Term Extraction
- Both input and output are both sequences, but the output is shorter(Many to Many)
- Speech Recognition
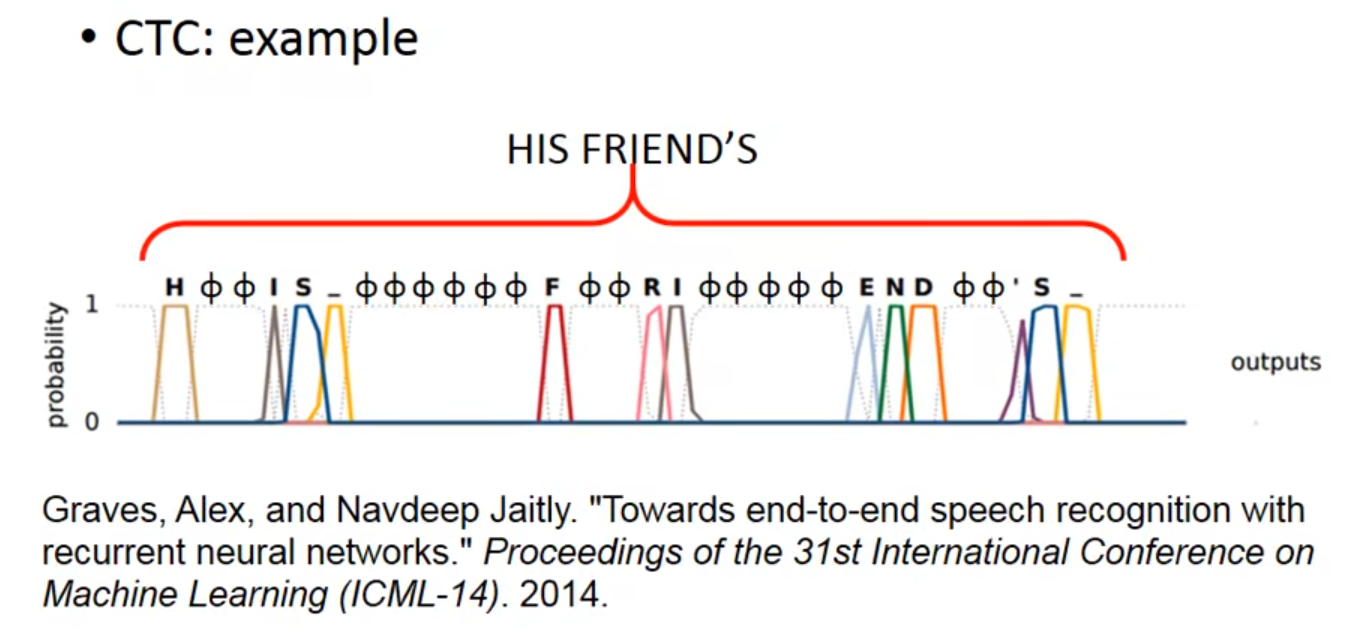
- Connectionist Temporal Classification(CTC)
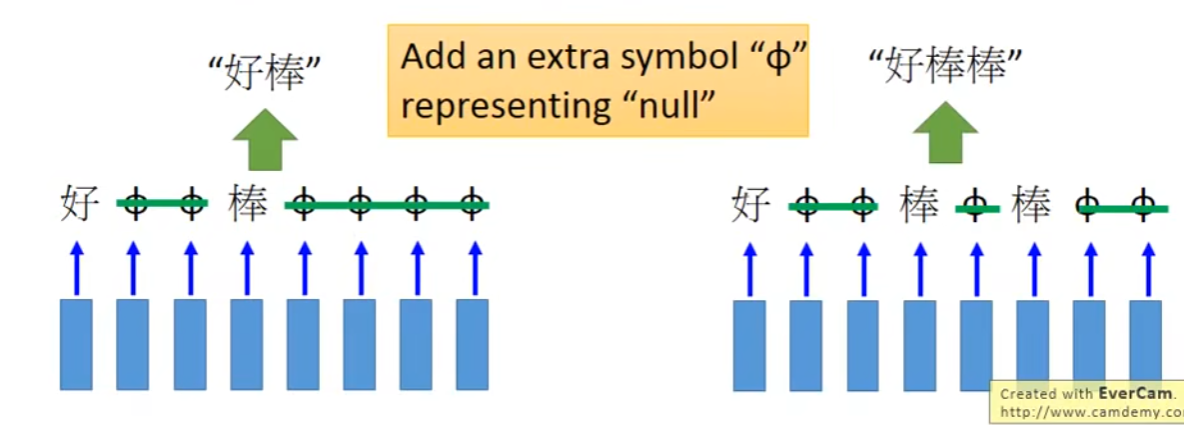
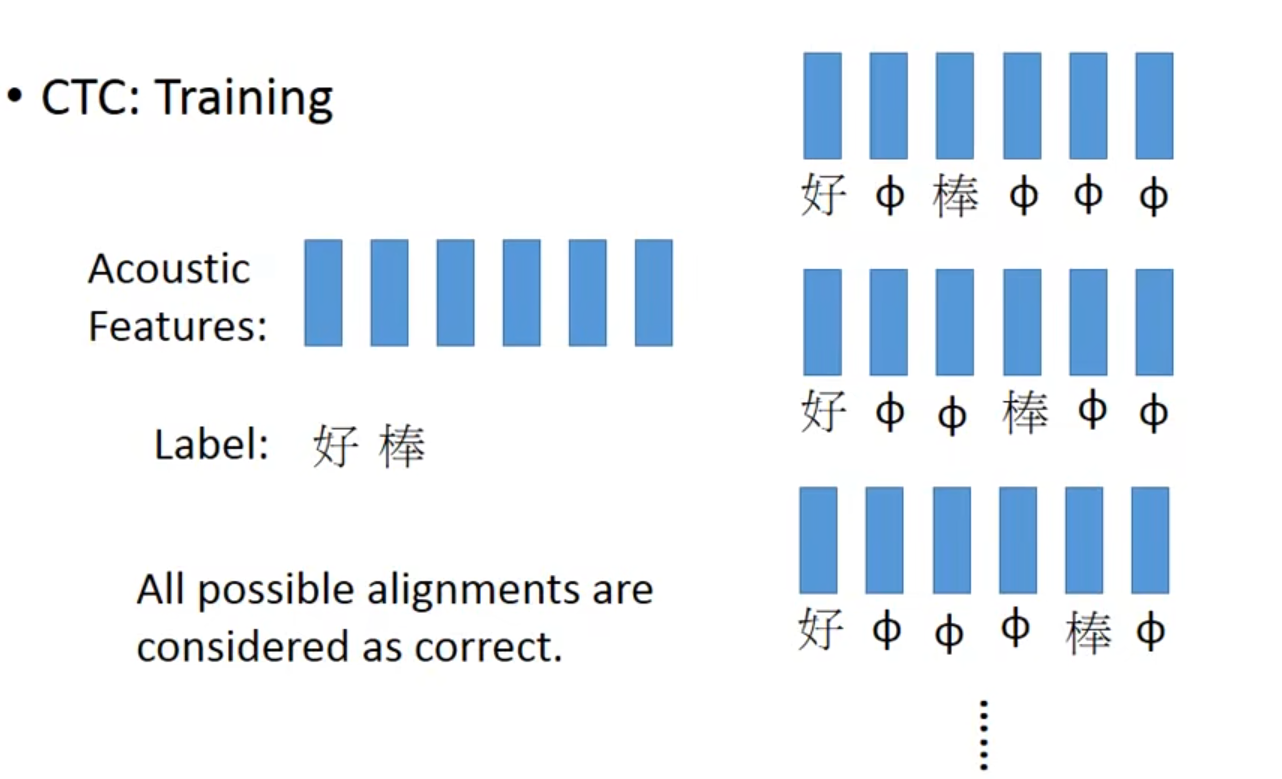
- 把右边三种结果都视为正确丢到training data中
- 机器不需要认识某个词汇
- Sequence to sequence learning(Many to Many(No Limitation))
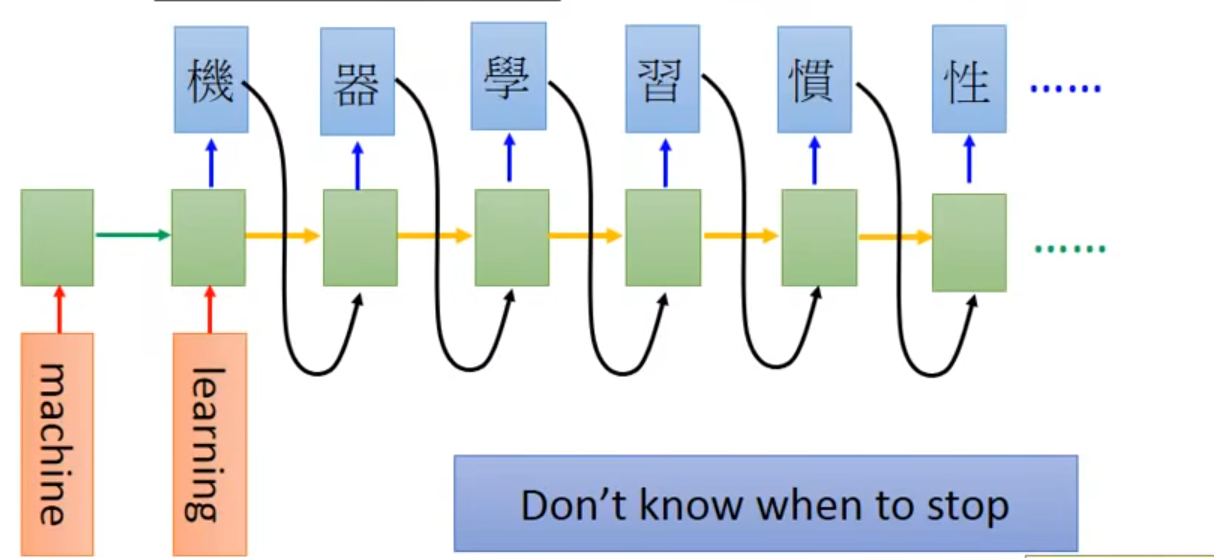
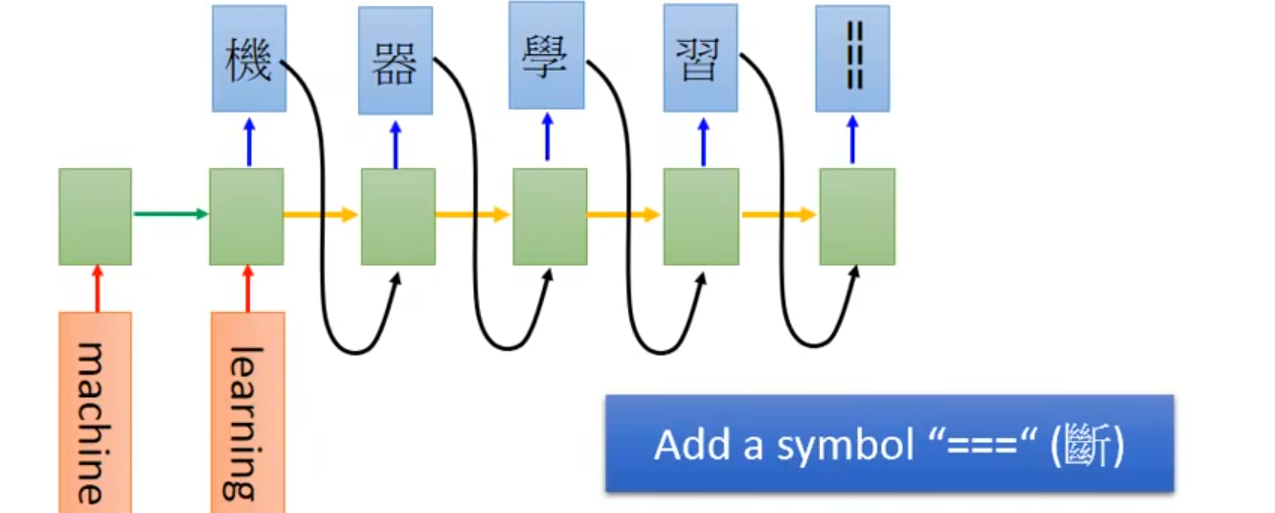
- RNN的input和output都是sequence,input和output的长度不确定。除此之外,在最后一个时间点,memory里存了所有input sequence的information,然后就让machine开始吐character,再将之前的output的character作为input,再读取上一个memory的值,继续output
- Problem:Don’t know when to stop

- Solution:Add a symbol “\=\=\=”断
- Sequence-to-sequence Auto-encoder
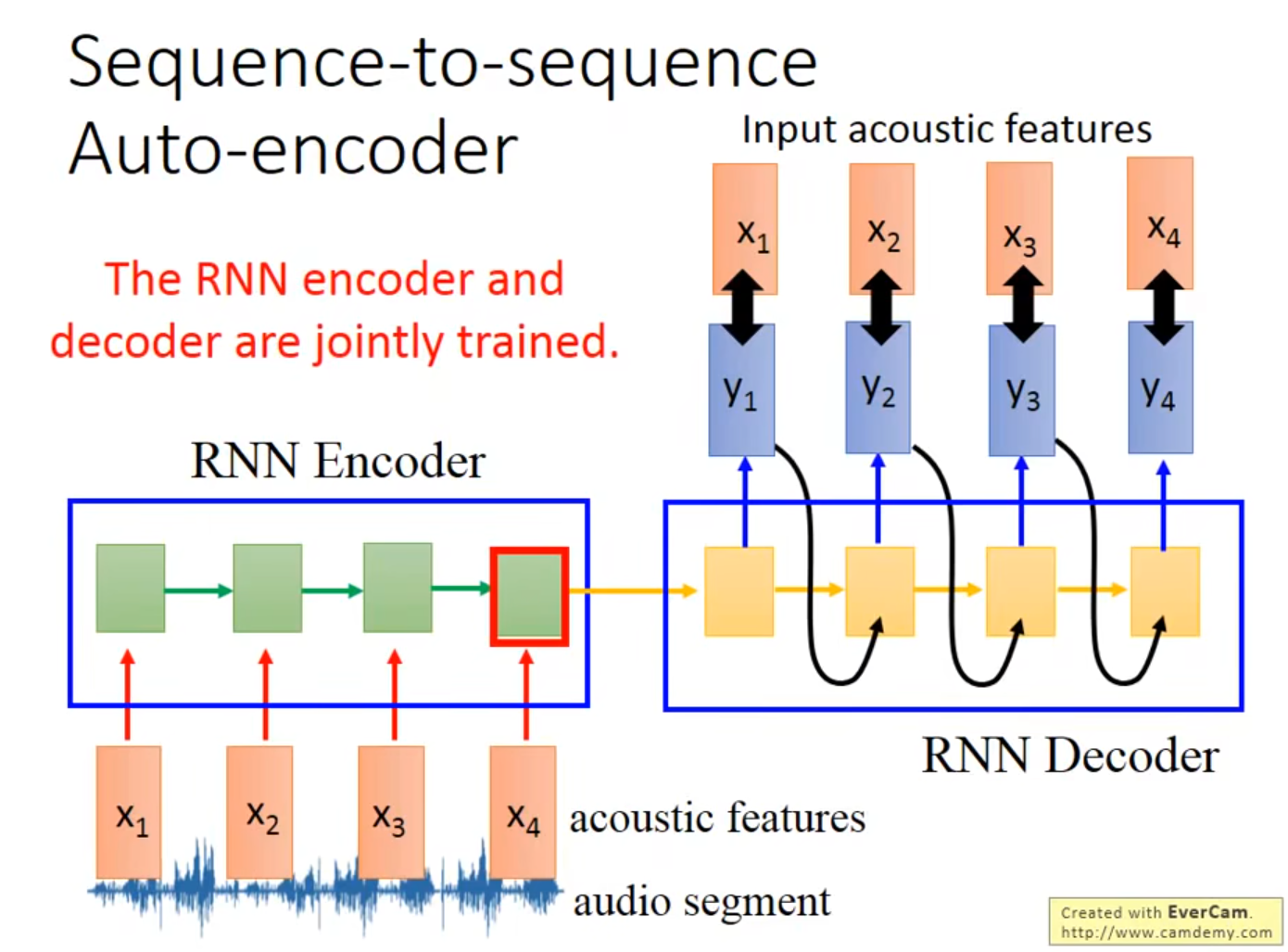
👆RNN Encoder和RNN Decoder是一起train的,目的是让train出来的$y_1$、$y_2$、$y_3$、$y_4$与$x_1$、$x_2$、$x_3$、$x_4$相近
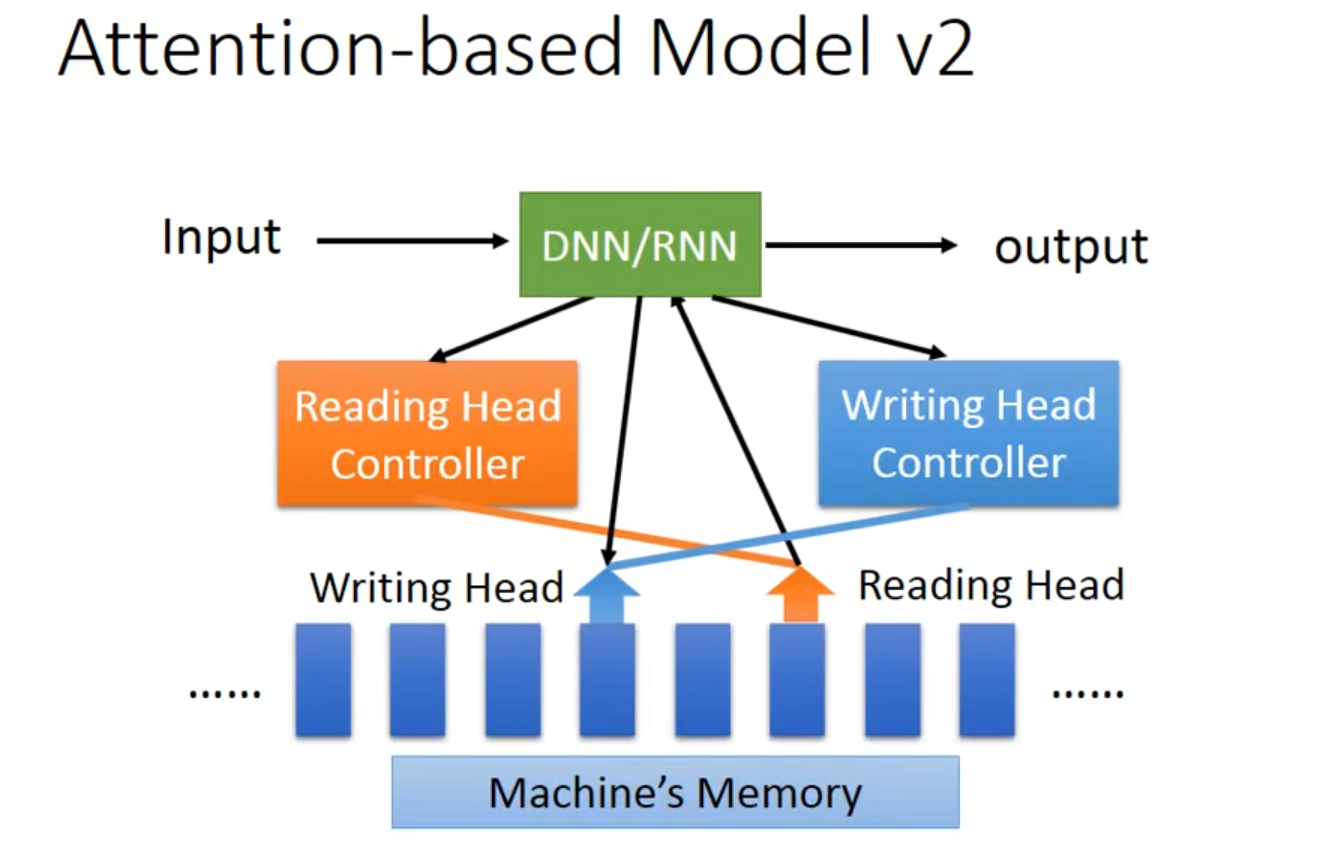
4.2 Attention-based Model
👇中央处理器DNN/RNN操控Reading Head Controller、读写头决定Reading Head放的位置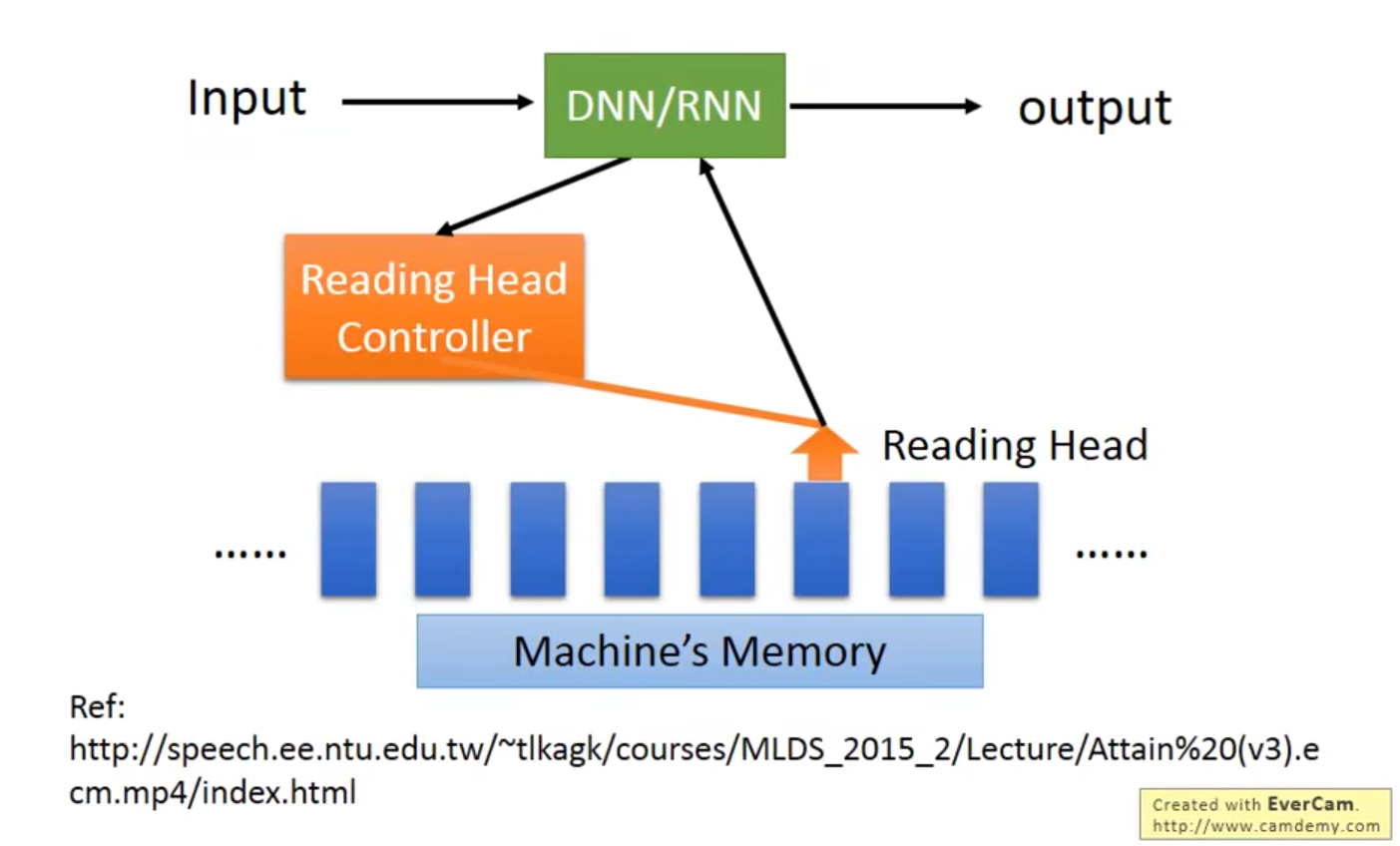
👇版本Ⅱ Neural Turing Machine(2014)